前几天和同事讨论问题,讨论到 RunLoop 时,发现这个基础概念已经快忘光了,这两天趁着需求完结的空档,整理重温一下。下面的源码来源于 Apple Source Browser CF-1153.18。
RunLoop
RunLoop 从字面直译运行循环,摘录苹果官方的介绍
Run loops are part of the fundamental infrastructure associated with threads. A run loop is an event processing loop that you use to schedule work and coordinate the receipt of incoming events. The purpose of a run loop is to keep your thread busy when there is work to do and put your thread to sleep when there is none.
简单总结就是,RunLoop 可以让你的线程在有任务时持续工作,在空闲时可以进入休眠,并能在有任务出现时及时被唤醒。
如果没有 RunLoop 线程在执行完自己的任务之后就会退出,如果希望在当前任务执行完毕线程不会退出,就需要一个合理的死循环让线程常驻。这样的机制被称为 Event Loop。这种机制并不是 Mac OSX 和 iOS 系统特有的,在绝大多数的系统框架都运用这一优良设计。
在 OSX 和 iOS 系统中,RunLoop 就是一个对象,两个系统的基础框架中提供两个这样的对象:NSRunLoop 和 CFRunLoopRef。
- CFRunLoopRef 是在 CoreFoundation 框架内的,它提供了纯 C 函数的 API,所有这些 API 都是线程安全的。
- NSRunLoop 是基于 CFRunLoopRef 的封装,提供了面向对象的 API,但是这些 API 不是线程安全的。
RunLoop 与线程
RunLoop 无法直接创建,但可以通过 CFRunLoopGetMain() 和 CFRunLoopGetCurrent() 来获取主线程或当前线程的 RunLoop 对象。这两个方法的内部都调用了 _CFRunLoopGet0(pthread_t t) 方法,传入的参数分别为 pthread_main_thread_np() 和 pthread_self(),也和 NSThread 中的 [NSThread mainThread] 和 [NSThread currentThread] 一一对应。继续看下 _CFRunLoopGet0(pthread_t t) 方法的内部,精简一下源码
static CFMutableDictionaryRef __CFRunLoops = NULL;
static CFLock_t loopsLock = CFLockInit;
CF_EXPORT CFRunLoopRef _CFRunLoopGet0(pthread_t t) {
if (pthread_equal(t, kNilPthreadT)) { // 1. 传入的参数如果为 nil,则默认为主线程
t = pthread_main_thread_np();
}
__CFLock(&loopsLock);
if (!__CFRunLoops) { // 2. 首次进入时,初始化全局的 Dict __CFRunLoops,并创建一个主线程对应的 run loop
__CFUnlock(&loopsLock);
CFMutableDictionaryRef dict = CFDictionaryCreateMutable(kCFAllocatorSystemDefault, 0, NULL, &kCFTypeDictionaryValueCallBacks);
CFRunLoopRef mainLoop = __CFRunLoopCreate(pthread_main_thread_np());
CFDictionarySetValue(dict, pthreadPointer(pthread_main_thread_np()), mainLoop);
CFRelease(mainLoop);
__CFLock(&loopsLock);
}
// 3. 从全局的 Dict 中获取当前线程对应的 run loop
CFRunLoopRef loop = (CFRunLoopRef)CFDictionaryGetValue(__CFRunLoops, pthreadPointer(t));
__CFUnlock(&loopsLock);
if (!loop) {
// 4. 如果全局 Dict 中不存在则创建新的 run loop 对象,并存储到全局 Dict 中
CFRunLoopRef newLoop = __CFRunLoopCreate(t);
__CFLock(&loopsLock);
loop = (CFRunLoopRef)CFDictionaryGetValue(__CFRunLoops, pthreadPointer(t));
if (!loop) {
CFDictionarySetValue(__CFRunLoops, pthreadPointer(t), newLoop);
loop = newLoop;
}
// don't release run loops inside the loopsLock, because CFRunLoopDeallocate may end up taking it
__CFUnlock(&loopsLock);
CFRelease(newLoop);
}
return loop;
}
RunLoop 与线程的关系是一一对应的,使用全局 Hash table __CFRunLoops 来保存 RunLoop 对象和线程的关系,使用线程作为 Key,RunLoop 对象本身为 Value。线程创建的时候并不会主动创建 RunLoop 对象,当我们去获取时才会创建。
RunLoop 的结构
在 CoreFoundation 的源码中,可以找到 RunLoop 的定义 __CFRunLoop。
struct __CFRunLoop {
...
CFMutableSetRef _commonModes;
CFMutableSetRef _commonModeItems;
CFRunLoopModeRef _currentMode; // 当前执行的 model
CFMutableSetRef _modes; // CFRunLoopModeRef 类型的集合 Set
...
};
从结构体的定义代码中,可以看出一个 RunLoop 对象可以拥有多个 CFRunLoopModeRef,而当前运行的 Mode 是唯一的。继续看下 CFRunLoopMode 的结构
typedef struct __CFRunLoopMode *CFRunLoopModeRef;
struct __CFRunLoopMode {
...
CFMutableSetRef _sources0;
CFMutableSetRef _sources1;
CFMutableArrayRef _observers;
CFMutableArrayRef _timers;
...
};
在 CFRunLoop.h 文件并没有找到 __CFRunLoopMode 结构体的声明,因此只能通过 CFRunLoopRef 提供的一些 API 对 CFRunLoopMode 中的 sources/observers/timers 进行操作。CoreFoundation 对外暴露了 __CFRunLoopSource __CFRunLoopObserver __CFRunLoopTimer 大致可以得出 RunLoop 的结构如下。

一个 RunLoop 对象可以包含多个 RunLoopMode,每个 RunLoopMode 又包含了多个 Sources/Observers/Timers。每次运行一个 RunLoop 都需要指定其中的一个 Mode,当前执行的 Mode 在 __CFRunLoop 结构体的 CFRunLoopModeRef _currentMode; 变量中。
__CFRunLoopSource
在 __CFRunLoopMode 的定义中,有两种 __CFRunLoopSource 的类型,_sources0 和 _sources1。
- Sources0 包含一个回调,但没有 mach port (mach 端口,后面会提到),这也就限制了 Sources0 无法主动触发事件,需要先使用
CFRunLoopSourceSignal(CFRunLoopSourceRef rls)将这个 source 标记为 Signaled,再手动调用CFRunLoopWakeUp(CFRunLoopRef rl)唤醒 RunLoop 执行这个 source。 - Sources1 不仅包含了回调,另外包含了
mach_port_t (*getPort)(void *info);可用于内核和其他线程相互发送消息,接收到消息时能够主动唤醒 RunLoop 的线程。
__CFRunLoopObserver
Observer 是观察者,每个 Observer 都包含一个回调 (函数指针)
typedef void (*CFRunLoopObserverCallBack)(CFRunLoopObserverRef observer, CFRunLoopActivity activity, void *info);
当 RunLoop 的执行状态发生变化的时候,会通过回调返回执行状态
/* Run Loop Observer Activities */
typedef CF_OPTIONS(CFOptionFlags, CFRunLoopActivity) {
kCFRunLoopEntry = (1UL << 0), // 即将进入 RunLoop
kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers = (1UL << 1), // 即将处理 Timers
kCFRunLoopBeforeSources = (1UL << 2), // 即将处理 Sources
kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting = (1UL << 5), // 即将进入休眠
kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting = (1UL << 6), // 刚从休眠中被唤醒
kCFRunLoopExit = (1UL << 7), // 即将退出 RunLoop
};
__CFRunLoopTimer
先来看一下 CFRunLoop.h 中对 __CFRunLoopTimer 的 typedef
typedef struct CF_BRIDGED_MUTABLE_TYPE(NSTimer) __CFRunLoopTimer * CFRunLoopTimerRef;
__CFRunLoopTimer 和 NSTimer 是 toll-free bridged 的,可以互相进行转换使用。其中包含一个时间点和一个回调,被加入 RunLoop 之后,当注册的时间点到时,RunLoop 会被唤醒以执行那个回调。
上述 Source/Observer/Timer 被统称为 mode item,mode 与 item 的关系为 1 对多的,但一个 item 被多次加入同一个 mode 时是无效的。
RunLoop 的运行
CoreFoundation 提供了两个运行 RunLoop 的方法
// 在 kCFRunLoopDefaultMode 下运行 RunLoop
void CFRunLoopRun(void) { /* DOES CALLOUT */
int32_t result;
do {
result = CFRunLoopRunSpecific(CFRunLoopGetCurrent(), kCFRunLoopDefaultMode, 1.0e10, false);
CHECK_FOR_FORK();
} while (kCFRunLoopRunStopped != result && kCFRunLoopRunFinished != result);
}
// 在指定的 mode 下运行 RunLoop
SInt32 CFRunLoopRunInMode(CFStringRef modeName, CFTimeInterval seconds, Boolean returnAfterSourceHandled) { /* DOES CALLOUT */
CHECK_FOR_FORK();
return CFRunLoopRunSpecific(CFRunLoopGetCurrent(), modeName, seconds, returnAfterSourceHandled);
}
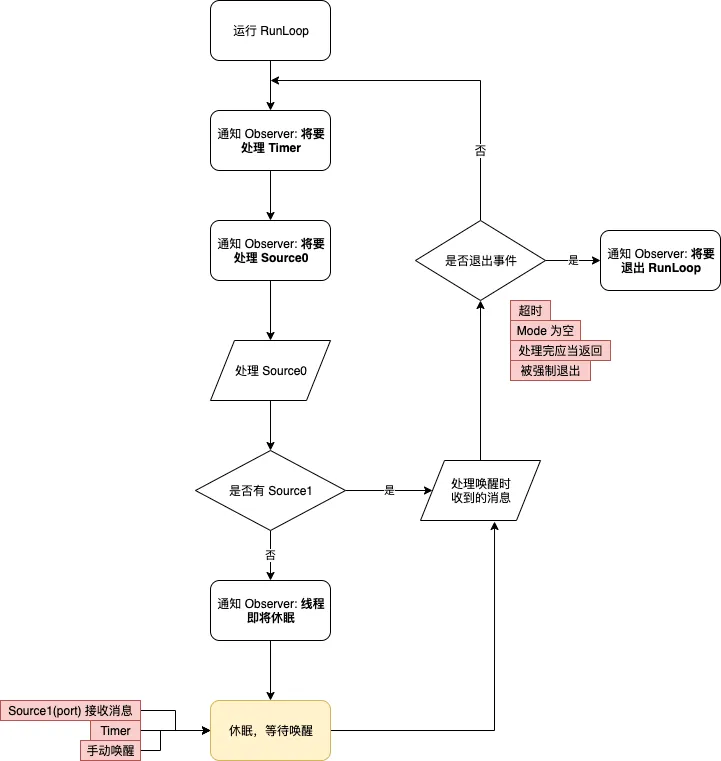
摘录官方文档的介绍,RunLoop 的内部运行逻辑大致如下。
- Notify observers that the run loop has been entered.
- Notify observers that any ready timers are about to fire.
- Notify observers that any input sources that are not port based are about to fire.
- Fire any non-port-based input sources that are ready to fire.
- If a port-based input source is ready and waiting to fire, process the event immediately. Go to step 9.
- Notify observers that the thread is about to sleep.
- Put the thread to sleep until one of the following events occurs:
- An event arrives for a port-based input source.
- A timer fires.
- The timeout value set for the run loop expires.
- The run loop is explicitly woken up.
- Notify observers that the thread just woke up.
- Process the pending event.
- If a user-defined timer fired, process the timer event and restart the loop. Go to step 2.
- If an input source fired, deliver the event.
- If the run loop was explicitly woken up but has not yet timed out, restart the loop. Go to step 2.
- Notify observers that the run loop has exited.
简单整理翻译下,画个流程图
实际执行 RunLoop 的源码行数过多,直接看容易懵逼,所以删减一些,保留一些关键步骤加上一些注释。
SInt32 CFRunLoopRunSpecific(CFRunLoopRef rl, CFStringRef modeName, CFTimeInterval seconds, Boolean returnAfterSourceHandled) {
// 依据 modeName 获取 currentMode
CFRunLoopModeRef currentMode = __CFRunLoopFindMode(rl, modeName, false);
// currentMode 为空或 currentMode 中 sources/timers/observers 为空,直接 return
if (NULL == currentMode || __CFRunLoopModeIsEmpty(rl, currentMode, rl->_currentMode)) {
Boolean did = false;
if (currentMode) __CFRunLoopModeUnlock(currentMode);
__CFRunLoopUnlock(rl);
return did ? kCFRunLoopRunHandledSource : kCFRunLoopRunFinished;
}
int32_t result = kCFRunLoopRunFinished;
// 1. Notify observers that the run loop has been entered.
// 通知 observer: RunLoop 即将进入
if (currentMode->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopEntry ) __CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, currentMode, kCFRunLoopEntry);
// 执行 RunLoop
result = __CFRunLoopRun(rl, currentMode, seconds, returnAfterSourceHandled, previousMode);
return result;
// 10. Notify observers that the run loop has exited.
// 通知 observer: RunLoop 即将退出 kCFRunLoopExit
if (currentMode->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopExit ) __CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, currentMode, kCFRunLoopExit);
return result;
}
// 运行 RunLoop
static int32_t __CFRunLoopRun(CFRunLoopRef rl, CFRunLoopModeRef rlm, CFTimeInterval seconds, Boolean stopAfterHandle, CFRunLoopModeRef previousMode) {
int32_t retVal = 0;
do {
// 2. Notify observers that any ready timers are about to fire.
// 通知 observer: 即将执行 Timers
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, rlm, kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers);
// 3. Notify observers that any input sources that are not port based are about to fire.
// 通知 observer: 即将触发 Source0 回调
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, rlm, kCFRunLoopBeforeSources);
// 执行被加入的 Blocks
__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(rl, rlm);
// 4. Fire any non-port-based input sources that are ready to fire.
// RunLoop 触发 Source0 (非 port) 回调。
Boolean sourceHandledThisLoop = __CFRunLoopDoSources0(rl, rlm, stopAfterHandle);
// 执行被加入的 Blocks
if (sourceHandledThisLoop) {
__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(rl, rlm);
}
// 5. If a port-based input source is ready and waiting to fire, process the event immediately. Go to step 9.
// 基于 mach_port 的事件处于 ready,立即处理 Source1,并跳转到 step 9。
if (MACH_PORT_NULL != dispatchPort && !didDispatchPortLastTime) {
msg = (mach_msg_header_t *)msg_buffer;
if (__CFRunLoopServiceMachPort(dispatchPort, &msg, sizeof(msg_buffer), &livePort, 0, &voucherState, NULL)) {
goto handle_msg;
}
}
// 6. Notify observers that the thread is about to sleep.
// 通知 observer: RunLoop 的线程即将进入休眠
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, rlm, kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting);
// 7. Put the thread to sleep until one of the following events occurs:
// 1. An event arrives for a port-based input source.
// 2. A timer fires.
// 3. The timeout value set for the run loop expires.
// 4. The run loop is explicitly woken up.
// RunLoop 的线程进入休眠,直到下列事件中的一个事件发生时,再唤醒
// 1. 基于 mach port 的 Source1 事件
// 2. Timer 的时间到了
// 3. RunLoop 超时
// 4. 被其他方式主动唤醒
//
// __CFRunLoopServiceMachPort 内部调用 mach_msg 方法,等待接收 mach_port 的消息
__CFRunLoopServiceMachPort(waitSet, &msg, sizeof(msg_buffer), &livePort, poll ? 0 : TIMEOUT_INFINITY, &voucherState, &voucherCopy);
// 8. Notify observers that the thread just woke up.
// 通知 observer: RunLoop 的线程刚刚被唤醒
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, rlm, kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting);
// 处理消息
handle_msg;
// 9.1 到达 timer 设定的时间,触发 timer 回调
if (port == _timerPort) {
__CFRunLoopDoTimers(rl, rlm, mach_absolute_time())
}
// 9.2 __CFTSDKeyIsInGCDMainQ 如果 dispatch 到 GCD main_queue 的 block,执行它
else if (port == dispatchPort) {
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_SERVICING_THE_MAIN_DISPATCH_QUEUE__(msg);
}
// 9.3 基于 mach_port 的 Source1 事件
else {
CFRunLoopSourceRef rls = __CFRunLoopModeFindSourceForMachPort(rl, rlm, livePort);
mach_msg_header_t *reply = NULL;
sourceHandledThisLoop = __CFRunLoopDoSource1(rl, rlm, rls, msg, msg->msgh_size, &reply) || sourceHandledThisLoop;
if (NULL != reply) {
(void)mach_msg(reply, MACH_SEND_MSG, reply->msgh_size, 0, MACH_PORT_NULL, 0, MACH_PORT_NULL);
}
}
// 执行被加入的 Blocks
__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(rl, rlm);
if (sourceHandledThisLoop && stopAfterHandle) {
// 参数声明执行完毕就返回
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunHandledSource;
} else if (timeout_context->termTSR < mach_absolute_time()) {
// 超出参数要求的超时时间
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunTimedOut;
} else if (__CFRunLoopIsStopped(rl)) {
// 外部调用强制停止
__CFRunLoopUnsetStopped(rl);
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunStopped;
} else if (rlm->_stopped) {
// 外部调用强制停止
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunStopped;
} else if (__CFRunLoopModeIsEmpty(rl, rlm, previousMode)) {
// mode items 为空
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunFinished;
}
} while (0 == retVal);
return retVal
}
__CFRunLoopRun 方法内部维护了一个 do-while 循环。线程一直停留在这个循环中,直到超时或者被手动停止,函数才会返回。
基于 RunLoop 实现的功能
在平时的开发工作中,有许多功能的实现都是基于 RunLoop 实现的,例如 AutoReleasePool,事件响应,手势识别等等,这些后面日后再来补充吧。